# To :is() or not to :is()?
Consider the following complex selectors:
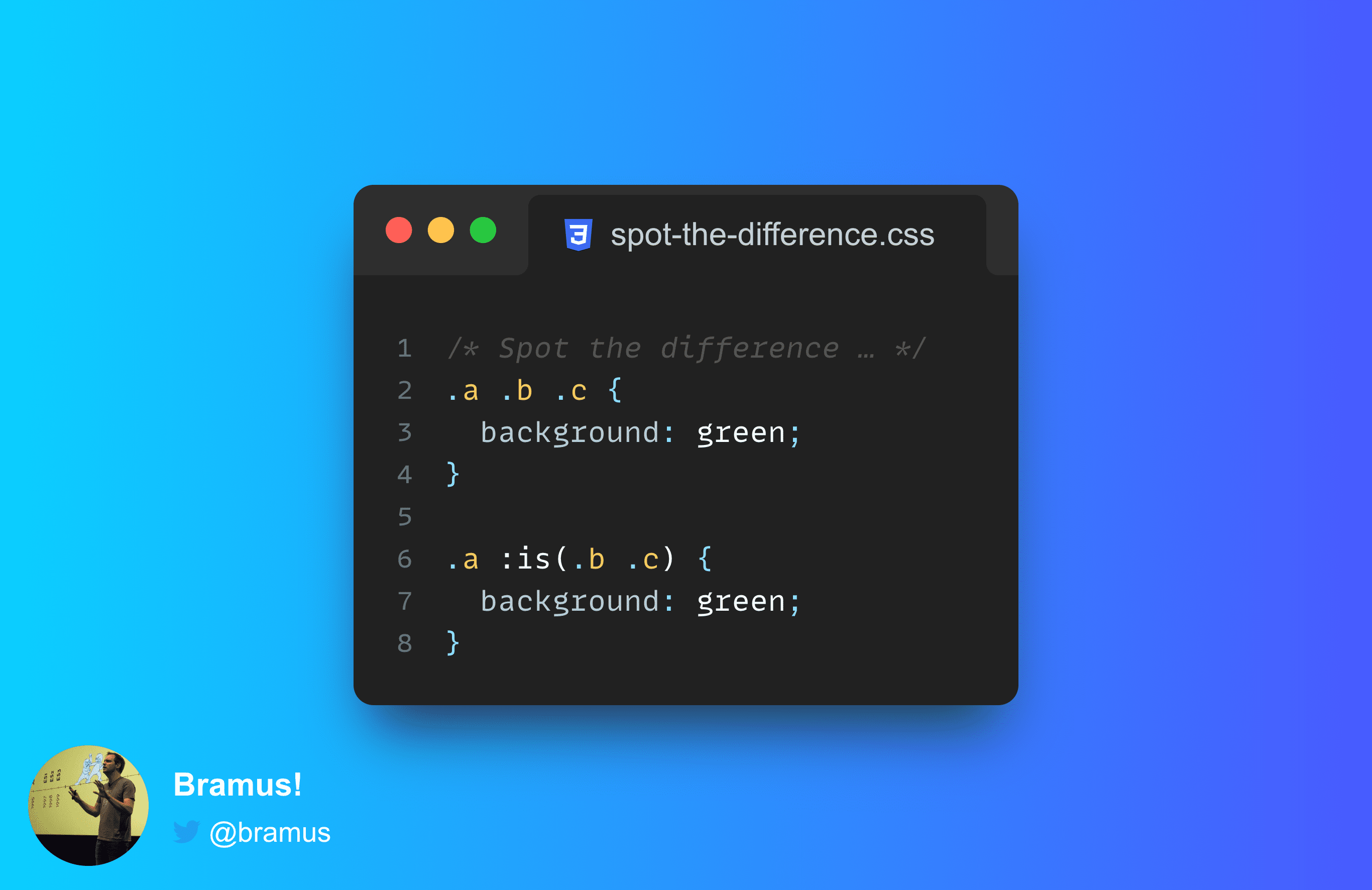
.a .b .c {
background: green;
}.a :is(.b .c) {
background: green;
}They might look the same, but they behave differently … the second selector selects more than you might initially think.
~
# Try it out
In this demo below there’s two nested pieces of markup:
<div class="a">
<div class="b">
<div class="c"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="b">
<div class="a">
<div class="c"></div>
</div>
</div>Use the dropdown to see which elements the .a .b .c and .a :is(.b .c) selectors match.
See the Pen CSS Nesting: The implications of :is() by Bramus (@bramus) on CodePen.
When choosing .a .b .c the first .c gets selected. But when choosing .a :is(.b .c) you’ll notice that both are selected … and to many that is very surprising.
~
# Explanation
Selector matching in browsers happens from right to left. That means that for these complex selectors the browser will start with the last <complex-selector-unit> (= spec lingo to indicate the individual parts, excluding the combinators) and then move up the chain.
.a .b .c-
This selector contains 3 units:
.a,.b, and.c. When trying to find matching elements, the browser will first select all.celements and will then check if they have a.bparent. If that’s the case, it will then check if that.bis a child of a.aelement. .a :is(.b .c)-
This selector contains 2 units:
.a, and:is(.b .c). The first evaluated unit:is(.b .c), which matches the.celements that have a.bancestor. If that’s true, the browser will then continue and check if that matched element – the.c– also has a.aancestor.
So that .a :is(.b .c) will match all of the .c elements in the snippet shown earlier, as the selector translates to “find me the .c elements that have both a .b and a .a as its ancestors”. That means it will also match this .c:
<div class="a b">
<div class="c"></div>
</div>If you can’t follow there, know that .a :is(.b .c) essentially desugars to this set of selectors:
.a .b .c.b .a .c.a.b .c
~
# Why is this relevant?
While I wouldn’t write a selector like that myself, this is highly relevant because of CSS Nesting that is getting specified. There, the Nesting Selector (&) desugars to :is().
Consider this nested block:
.b .c {
.a & {
background: green;
}
}When desugaring & to the outer selector wrapped inside a :is(), that snippet would become:
.a :is(.b .c) {
background: green;
}This might be counterintuitive for authors who have used Sass and other preprocessors before. In Sass, the & simply gets replaced with the outer selector:
.a .b .c {
background: green;
}As demonstrated earlier in this post, these behave differently.
~
# Anything else about :is()?
As mentioned in an earlier post, there’s more things to know about :is():
- The selector list of
:is()is forgiving - The specificity of
:is()is that of its most specific argument :is()does not work with pseudo-element selectors (for now)
See https://brm.us/css-is for more details
~
# Spread the word
To help spread the contents of this post, feel free to retweet its announcement tweet:
Using `:is()` in complex selectors selects more than you might initially think.
🏷 #css #selectors pic.twitter.com/uN9wIAZ2Zm
— Bram.us (@bramusblog) January 17, 2023
~
🔥 Like what you see? Want to stay in the loop? Here's how:
Leave a comment