We’re all doomed:
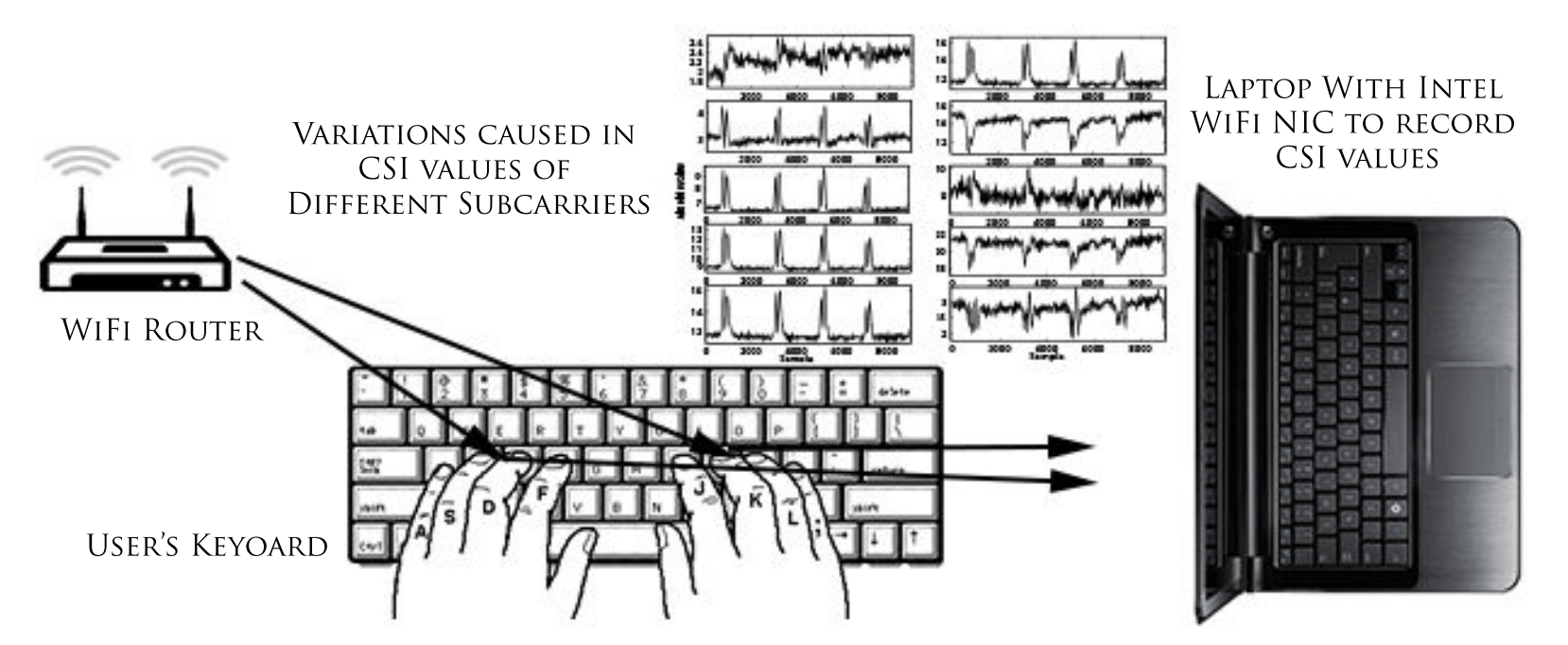
In this paper, we propose a WiFi signal based keystroke recognition system called WiKey. WiKey consists of two Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) WiFi devices, a sender (such as a router) and a receiver (such as a laptop). The sender continuously emits signals and the receiver continuously receives signals. When a human subject types on a keyboard, WiKey recognizes the typed keys based on how the CSI values at the WiFi signal receiver end.
Obviously that must not be accurate at all, right? Erm, wrong:
WiKey achieves more than 97.5% detection rate for detecting the keystroke and 96.4% recognition accuracy for classifying single keys. In real-world experiments, WiKey can recognize keystrokes in a continuously typed sentence with an accuracy of 93.5%.